Give the 2‐D Transformation matrix for a) Translation b) Rotation c) scaling
2D Transformation Matrix
One of the most common and important tasks in computer graphics is to transform the coordinates (position, orientation, and size) of either object within the graphical scene or the camera that is viewing the scene. It is also frequently necessary to transform coordinates from one coordinate system to another, (e.g. world coordinates to viewpoint coordinates to screen coordinates.) All of these transformations can be efficiently handled using some simple matrix representations, which we will see can be particularly useful for combining multiple transformations into a single composite transform matrix.
The general procedures for applying translation, rotation, and scaling Parameters to reposition and resize the two-dimensional objects.
a)Translation:-
Translation is a process of changing the position of an object in a straight-line path from one coordinate location to another. We can translate a two dimensional Point by adding translation distances tx and ty, to the original coordinate position (x, y) to move the point to a new position (x’, y’) as shown in the figure (a).
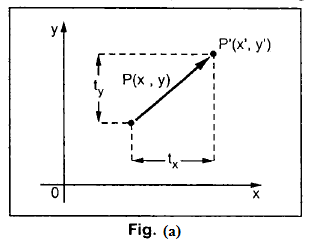
The translation distance pair (tx , ty) is called a translation vector or shift vector.
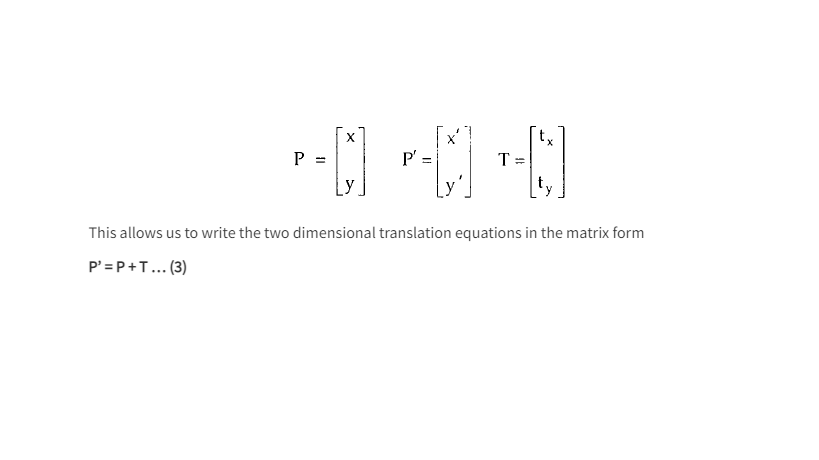
It is possible to express the translation equations 1 and 2 as a single matrix equation by using column vectors to represent coordinate Positions and the translation vector:
b)Rotation:-
A two dimensional rotation is applied to an object by repositioning it along a circular path in the xy plane. To generate a rotation we specify a rotation angle θ and the position of the rotation point about which the object is to be rotated.
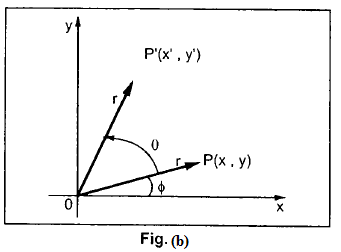
Let us consider the rotation of the object about the origin, as shown in the figure (b). Here, r is the constant distance of the point from the origin, angle ∅ is the original angular position of the point from the horizontal, and θ is the rotation angle. Using standard trigonometric equations, we can express the transformed coordinates in terms of angles θ and ∅ as


c) Scaling :-
A scaling transformation changes the size of an object.This operation can be carried out for polygons by multiplying the coordinate values (x, y) of each vertex by scaling factors Sx and Sy,to Produce the transformed coordinates (x’, y’)

