Explain the Order-Statistic Filters.
There are four types of Order-Statistic filters. They are
(i) Median filter
The best-known order-statistics filter is the median filter, which, as its name implies, replaces the value of a pixel by the median of the gray levels in the neighborhood of that pixel:
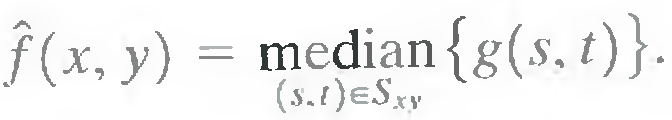
The original value of the pixel is included in the computation of the median. Median filters are quite popular because, for certain types of random noise, they provide excellent noise-reduction capabilities, with considerably less blurring than linear smoothing filters of similar size. Median filters are particularly effective in the presence of both bipolar and unipolar impulse noise.
(2) Max and min filters
Although the median filter is by far the order-statistics filler most used in image processing, it is by no means the only one. The median represents the 50th percentile of a ranked set of numbers, but the reader will recall from basic statistics that ranking lends itself to many other possibilities. For example, using the 100th percentile results in the so-called max filter, given by
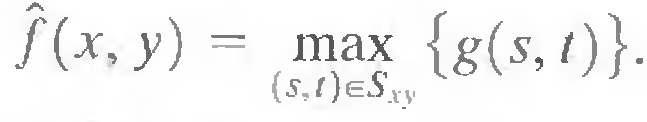
This filter is useful for finding the brightest points in an image. Also, because pepper noise has very low values, it is reduced by this filter as a result of the max selection process in the subimage area Sxy.
The 0th percentile filter is the min filter.
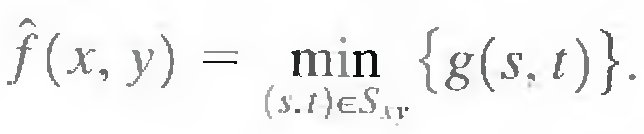
This filter is useful for finding the darkest points in an image. Also, it reduces salt noise as a result of the min operation.
(3) Midpoint filter
The midpoint filter simply computes the midpoint between the maximum and minimum values in the area encompassed by the filter:
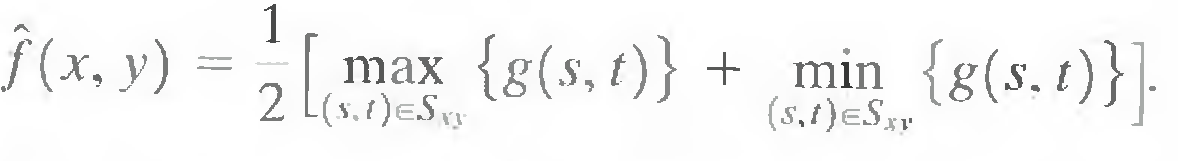
Note that this filter combines order statistics and averaging. This filter works best for randomly distributed noise, like Gaussian or uniform noise.
(4) Alpha - trimmed mean filter
It is a filter formed by deleting the d/2 lowest and the d/2 highest gray-level values of g(s, t) in the neighborhood Sxy. Let gr (s, t) represent the remaining mn - d pixels. A filter formed by averaging these remaining pixels is called an alpha-trimmed mean filter:

where the value of d can range from 0 to mn - 1. When d = 0, the alpha- trimmed filter reduces to the arithmetic mean filter. If d = (mn - l)/2, the filter becomes a median filter. For other values of d, the alpha-trimmed filter is useful in situations involving multiple types of noise, such as a combination of salt-and-pepper and Gaussian noise.